Best
Nephrology
See the World Clearly: Your Ophthalmology & Eye Care Resource Center
Welcome to your one-stop shop for all things related to eye health and ophthalmology! Whether you're experiencing vision problems, seeking preventative care tips, or simply curious about the fascinating world of the eyes, you've come to the right place.
About Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology is a branch of medicine specializing in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of eye diseases and disorders. Ophthalmologists are medical doctors who have completed additional training in eye care and are qualified to perform surgery, prescribe medications, and manage a wide range of eye conditions.
Common Eye Conditions:
- Refractive Errors: Nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism are common vision problems corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or LASIK surgery.
- Glaucoma: This group of eye diseases damages the optic nerve, potentially leading to vision loss. Early detection and treatment are crucial.
- Cataracts: A clouding of the lens that can blur vision. Cataract surgery is a safe and effective procedure to restore clear vision.
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): A leading cause of vision loss in adults, AMD affects the central vision.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes can damage blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems. Regular eye exams are essential for people with diabetes.
Maintaining Healthy Eyes:
- Schedule Regular Eye Exams: Comprehensive eye exams are crucial for detecting eye problems early on, even if you're not experiencing any symptoms.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help promote eye health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a risk factor for several eye diseases.
- Protect Your Eyes from UV Rays: Wear sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays to shield your eyes from sun damage.
- Limit Screen Time: Take breaks from screens like computers and phones to reduce eye strain.
- Don't Smoke: Smoking increases the risk of developing eye diseases.
Ophthalmology: Understanding and Caring for Eye Health
What is Ophthalmology?
Ophthalmology is the branch of medicine and surgery that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of eye disorders. Ophthalmologists are medical doctors specializing in eye and vision care, performing eye exams, diagnosing and treating diseases, prescribing medications, and performing eye surgery.
Common Eye Conditions and Diseases
Refractive Errors
- Myopia (Nearsightedness): Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly.
- Hyperopia (Farsightedness): Difficulty seeing close objects clearly.
- Astigmatism: Distorted vision caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens.
- Presbyopia: Age-related difficulty in seeing close objects due to loss of lens elasticity.
Cataracts
- Cataracts: Clouding of the eye’s lens, leading to decreased vision. Common in older adults.
Glaucoma
- Glaucoma: A group of diseases that damage the eye's optic nerve, often associated with high intraocular pressure, leading to vision loss and blindness if untreated.
Macular Degeneration
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Deterioration of the central portion of the retina (macula), affecting central vision.
Diabetic Eye Disease
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina due to high blood sugar levels, leading to vision problems and blindness.
Retinal Disorders
- Retinal Detachment: Separation of the retina from the underlying tissue, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Retinitis Pigmentosa: A group of genetic disorders causing retinal degeneration and vision loss.
Corneal Diseases
- Keratitis: Inflammation of the cornea, often due to infection.
- Keratoconus: A condition where the cornea thins and bulges outward, causing distorted vision.
Eye Infections and Inflammations
- Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, the clear tissue covering the white part of the eye and the inside of the eyelids.
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye.
Dry Eye Syndrome
- Dry Eye: Insufficient lubrication and moisture on the eye’s surface, causing discomfort and vision problems.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques in Ophthalmology
Visual Acuity Tests
- Snellen Chart: Measures how well you see at a distance.
- Refraction Assessment: Determines the prescription for glasses or contact lenses.
Tonometry
- Tonometry: Measures intraocular pressure to detect glaucoma.
Ophthalmoscopy
- Fundoscopy: Examines the back of the eye, including the retina, optic disc, and blood vessels.
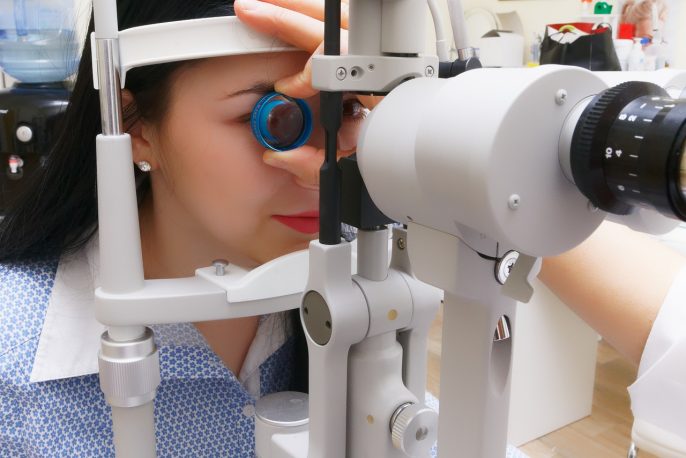
Slit-Lamp Examination
- Slit-Lamp: A microscope with a bright light used to examine the structures of the eye in detail.
Imaging Techniques
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Non-invasive imaging test providing cross-sectional images of the retina.
- Fluorescein Angiography: Uses a fluorescent dye to visualize blood flow in the retina and choroid.
Visual Field Testing
- Perimetry: Measures peripheral vision and detects blind spots.
Common Treatments and Interventions in Ophthalmology
Medications
- Eye Drops: Used to treat various conditions such as glaucoma, infections, and inflammation.
- Oral Medications: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and other medications for systemic eye conditions.
Corrective Lenses
- Eyeglasses: Correct refractive errors and improve vision.
- Contact Lenses: Alternative to eyeglasses for vision correction.
Surgical Procedures
- Cataract Surgery: Removal of the clouded lens and replacement with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
- LASIK: Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis, a procedure to reshape the cornea and correct refractive errors.
- Glaucoma Surgery: Procedures like trabeculectomy or laser surgery to reduce intraocular pressure.
- Vitrectomy: Removal of the vitreous gel from the eye, used to treat retinal detachment, macular holes, and other retinal conditions.
- Corneal Transplant: Replacement of a damaged cornea with a donor cornea.
Advances in Ophthalmology
Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Micro-Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS): Less invasive procedures to lower intraocular pressure with fewer complications.
Advanced Imaging
- Enhanced OCT: Provides detailed images of retinal layers for early detection of diseases.
Gene Therapy
- Luxturna: A gene therapy for treating certain genetic forms of blindness.
Artificial Intelligence
- AI Diagnostics: Using machine learning algorithms to detect and diagnose eye diseases from imaging studies.
Regenerative Medicine
- Stem Cell Therapy: Research into using stem cells to regenerate damaged retinal cells and restore vision.
Preventive Eye Care
Regular Eye Exams
- Routine Check-Ups: Essential for early detection and management of eye conditions.
Protective Eyewear
- Safety Glasses: Prevent eye injuries in hazardous environments.
- Sunglasses: Protect against harmful UV rays.
Healthy Lifestyle
- Diet and Nutrition: Consuming foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, and omega-3 fatty acids supports eye health.
- Smoking Cessation: Reduces the risk of cataracts, macular degeneration, and other eye diseases.
Conclusion
Ophthalmology is a critical field dedicated to maintaining and improving eye health through advanced diagnostic techniques, innovative treatments, and preventive care. Regular eye exams and early intervention are essential for preserving vision and preventing eye diseases. Consulting with a specialized ophthalmologist ensures comprehensive care for all eye-related concerns.
For more information, patients can refer to reputable sources such as the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) and the National Eye Institute (NEI).